Intelligent Car
Evaluation and Analysis
Specifications
The basic functionality of the car can be broken down into three small sub-components. It must be able to follow the black line accurately and change its turning direction based on a color coded marker. Lastly, it must perform three operation modes and the user must be able to select any mode at any time.
The car was able to perform as desired and a list of successful test results is listed below:
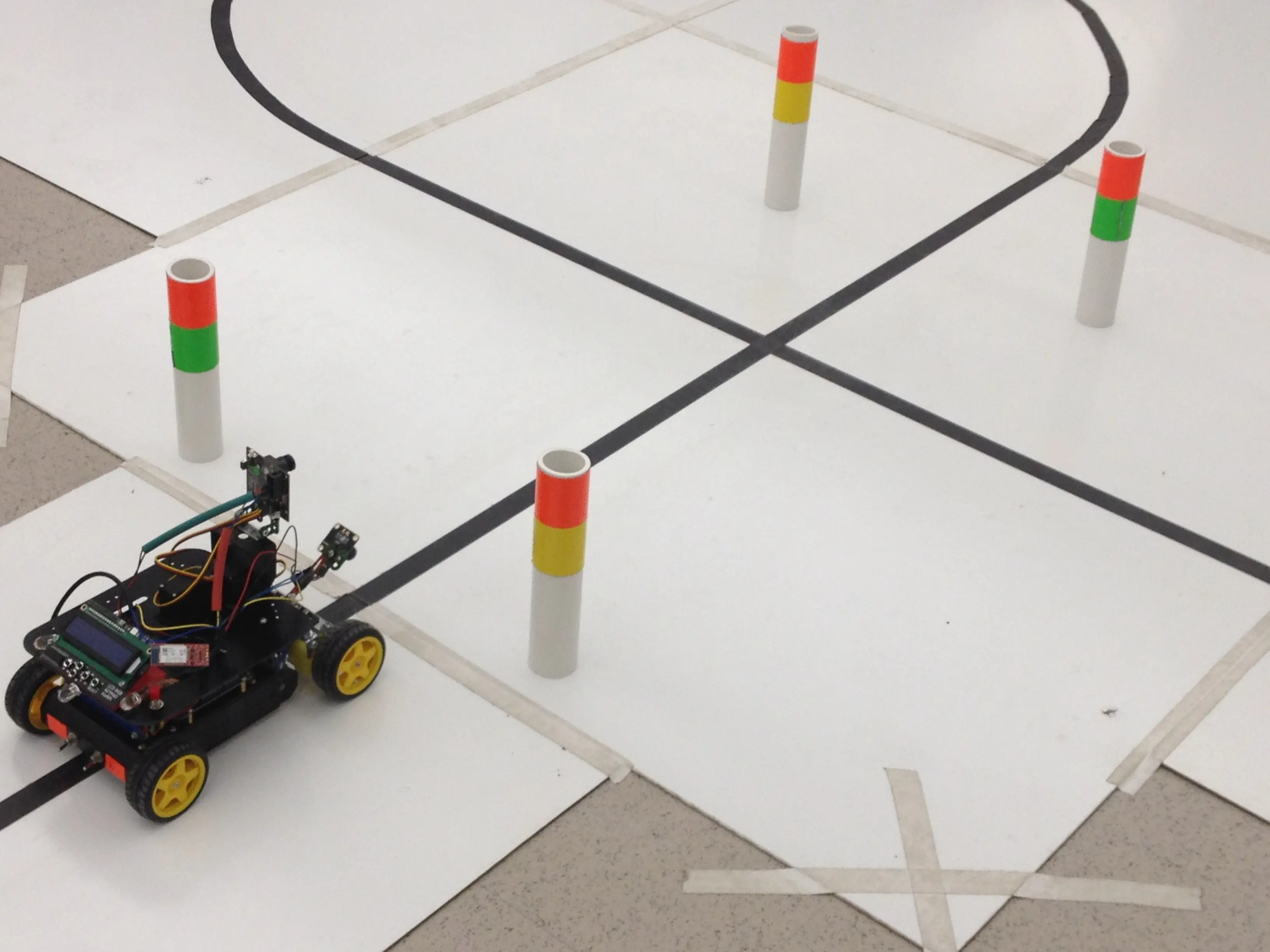
- The car tracks a black line against a white background
- The car navigates autonomously around on the track
- The car uses a line camera to detect a black line on the track
- The car uses vision sensor (CMUcam5 Pixy) to detect posts
- The car follows the commands from the posts which are located on the left and right sides of the track at the intersection on the track
- The car obeys the post closest to the intersection when more than one post is present
- The car moves when powered on
- The car changes the mode when the user interacts with the interface
- The car moves in the forward direction of the track
- The car follows the black line of the track as closely as possible
- The car stops while staying on the track within 1 meter of the stop line
- The data from the car can be logged and saved via an SD card or bluetooth.
- The car also has some optional features such as an LCD display for modes, blinkers, and brake lights. When the pixy camera recognizes a direction signature, the LED corresponding to that direction will turn on.
Additionally, the car is able to operate in the three operation modes after the user selects an operation mode. Some of the test results for every challenge are listed below.
Discovery Mode
- The car is placed within 2 ft. of the edge of any part of the track at any orientation
- The car starts searching for the track when commanded
- The car can locate the track within 3 minutes
- The car automatically restarts if it fails to locate the track within 3 minutes
Accuracy Mode
- The car is placed at the starting point on the track
- The car follows the black line of the track as closely as possible until it has completed two laps
- The car automatically stops after the completion of the second lap
Speed Mode
- The car is placed at the starting point on the track
- The car follows the black line of the track as closely as possible until it has completed two laps
- The car automatically stops after the completion of the second lap
- The car has no more than two trials to complete this challenge with at least one valid lap
Unique Innovations
The unique components of our car system make it possible for the car system to follow the black line with 95% accuracy at 85% speed setting with an average lap time of 1 minute and 10 seconds in accuracy mode while maintaining the car center with the line at any point. More unique system design are listed below:
- Our design uses a unique Hybrid driving controller that utilizes a front steering system and a standard differential. By implementing both of these components, the car is able to make sharper turns at higher speeds and turn on its on axis when an intersection is detected.
- LCD user Interface
- Signal Lights
- Our software design is very modular and very easy to read.
- A partial library was developed which acts similar to the HAL.
- Multiple structs and typedefs allow us to mimic classes.
Weaknesses
Below is a list of problems that we ran into while implementing the car system; however, these problems were fixed before the car system was delivered. However there were external problems outside of our control. A breakdown of the problems (weaknesses) are listed and described below:
Electromagnetic Interference
The car system chassis deign was made to be compact and user friendly. To accomplish this the circuit board which holds the H-Bridge and Power regulator components is mounted inside the car chassis along with the power distribution board. As a result, the electromagnetic noise from the driving motors interferes with the grounding system of the distribution board.
Under-steering
After the steering system was implemented, the car was able to make 90ᵒ turns, but it was unable to stay center with the line when turning in a circle or turning in an intersection. To solve this, the Hybrid drive system was implemented. (Descried in section 2.2.1)
Inconsistent Hardware
Physical switches sometimes caused the operation mode to change. In order to resolve this issue, we exerted caution when operating the physical switches. This problem can be caused by electrical noise in the ground line.
Lighting
Ambient light affects the detection of the intersection line or the start/stop line. This problem was encountered when testing during early hours in the morning. This can be solved by adjusting the angle of the line camera depending on the time of the day.